Efficient Modern Laboratory Systems Need 6 Essential Trends

Laboratory instruments are considered simple data generators to transform physical assessment into numbers. Most of us have experienced a conversion of laboratory data production and management schemes for years. However, the right data processing and specific tools are essential to efficiently refine raw data into analysis in making decisions.
A data management system is necessary to facilitate the collaboration of different instruments. Harmony and generating significant information have their own importance in operating your laboratory. Meanwhile, coordinating your laboratory’s data management practices needs investment and extraordinary efforts. The following 6 trends are essential to the most efficient labs.
Connect Lab Equipment to a Centralized Database
The automation of data collection to a centralized database has its own importance. The delivery of test data and results manually from a device to a storage database isn’t a good practice. Almost all the following discussed trends don’t recommend such activities. These non-value-add practices can discharge resources and demoralize efficiency.
You can store data in different places including Laboratory Management System (LIMS) for your own objectives. However, you can also use the Manufacturing Execution System (MES) to monitor the quality and production efficiency. But it depends on your organization’s laboratory functions. You must ask about their capability to integrate with your system to evaluate test instrument suppliers.
Meanwhile, some suppliers encourage this integration but others refuse. They often motivate their own developed data management system. But these types of solutions efficiently work within their product portfolios. They normally create barriers to achieving flawless and centralized data management architecture. We recommend engaging your IT resources to get an idea of their preferences to ensure integration.
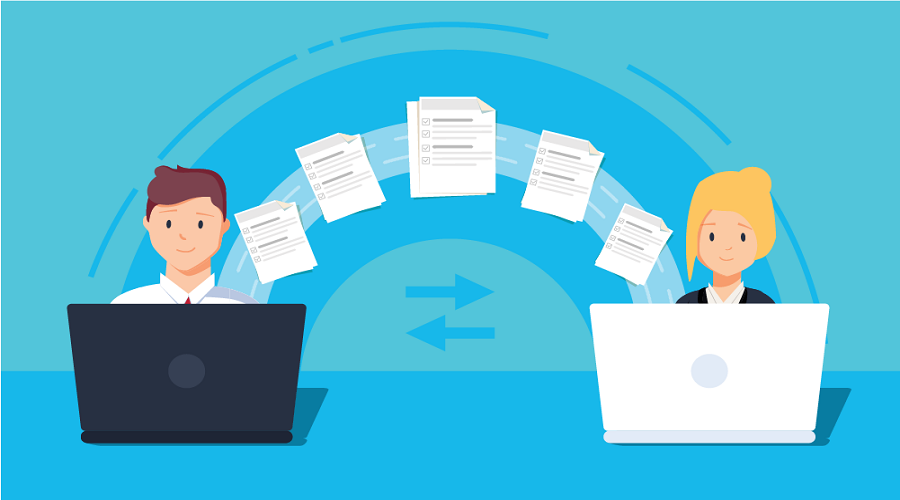
Enhance Timesaving using Bi-Directional Data Transfer
An excellent implementation of connected test instruments often needs a Bi-directional data transfer system. This system visualizes the unidirectional output of data when most people need data transferring. It allows scale measurement by connecting a computer to decrease manual data entry. You can press an export button on the scale. This will start transferring its mentioned pileup reading to a linked field on the computer.
This process is considered unidirectional or one-way communication. But bidirectional or two-way communication is efficient and commonly used with complicated instruments that need multiple inputs. Meanwhile, a material testing system needs inputs distinctive to the sample under test. It also requires production batch numbers, dimensional values, and the test type to control the system.
The Future is 2D Barcodes
The efficient automated mechanism is Barcodes, used to digitally move data linked with a test sample to a database. Many industries around the world used linear or 1D (one-dimensional) barcodes for identification applications. However, 2D (two-dimensional) barcodes have significant strong advantages that replaced linear barcodes. Two-dimensional barcodes contain 2,000 characters with carrying a smaller footprint but 1D contains around 25 characters.
Automated Instrument Maintenance Logistics
Managing the maintenance and adjustment processes is essential to keep your test instruments working efficiently. But it takes significant time to coordinate the logistics around these service visits. Meanwhile, the automation of scheduling of routine services needs more instruments to apply automatic recording. It would efficiently predict part failures to proactively reply and limit system downtime.
Expected Remote Management
The walls of your laboratory need restricted access to your lab’s data. If you are working from home and need to check the status of a test or want to share your data with a colleague. Remotely accessing instrument data has become an expectation. LIMS has its own benefits for centralizing data as the system is traditionally designed in a client/ server architecture. It enables users and instruments to read and write data stored on the central database.
Cybersecurity is More Essential
The risk of malicious data breaches has increased as the data increases, while storage is away from on-premises. Organizations need to run centralized data management systems more efficiently. Most operations can become a standoff if you don’t properly secure these systems. Cybersecurity susceptibilities can exist in any link of the chain, so effective security is essential to data management infrastructure.